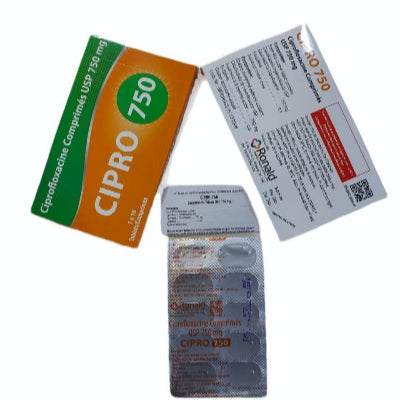
Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)
Cipro 750 mg contains ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic with potent activity against a broad range of Gram-negative bacteria and certain Gram-positive and atypical organisms. Ciprofloxacin inhibits bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which prevents DNA replication and leads to bacterial death. The 750 mg dose is commonly used for more serious or complicated infections and in cases where higher systemic exposure is required.
Ciprofloxacin should be used under medical supervision with awareness of its safety profile and potential drug interactions. It is typically reserved for infections where alternatives are unsuitable or where culture/sensitivity supports its use.
Product introduction
Ciprofloxacin is a well-established fluoroquinolone antibiotic available in oral and intravenous forms. The 750 mg oral tablet provides high systemic levels and is often used for complicated urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis), certain respiratory infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections when combined with other agents, and serious soft tissue or bone infections when appropriate.
Because fluoroquinolones have been linked to rare but serious adverse events, prescribers follow stewardship recommendations to use them only when clearly indicated and when benefits outweigh risks.
Uses of Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)
Cipro 750 mg may be prescribed for:
- Complicated urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis)
- Complicated intra-abdominal infections (usually as part of combination therapy)
- Certain cases of community-acquired or hospital-associated pneumonia when pathogen susceptibility supports use
- Severe skin and soft tissue infections (depending on organism)
- Bone and joint infections (specialist-guided therapy)
- Certain prostatitis cases
- Traveller’s diarrhea caused by susceptible organisms (selected cases)
Note: Ciprofloxacin is ineffective against viral infections and should be used guided by culture/sensitivity where possible.
Benefits of Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)
Why clinicians may choose ciprofloxacin 750 mg:
- Powerful Gram-negative coverage, including many Enterobacterales.
- High oral bioavailability allows outpatient step-down from IV therapy.
- Good tissue penetration into urinary tract, prostate, and soft tissues.
- Once- or twice-daily dosing depending on regimen and infection.
- Rapid bactericidal action against susceptible organisms.
In Treatment of Worm infections
Important: Ciprofloxacin is not anthelmintic and does not treat parasitic worm infections. This heading is included solely to preserve the page structure.
Side effects of Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)
Ciprofloxacin is generally effective but has a recognized side-effect profile. Many patients tolerate it well, but there are common and rare serious adverse effects you should be aware of.
Common side effects
- Nausea, vomiting
- Diarrhoea or abdominal discomfort
- Dizziness, headache
- Sleep disturbance
- Skin rash or photosensitivity
Serious but rare: tendonitis and tendon rupture (including Achilles tendon), peripheral neuropathy (paresthesia or numbness which can be persistent), central nervous system effects (confusion, hallucinations, seizures), QT prolongation (cardiac rhythm disturbances), severe hypersensitivity reactions, and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhoea. Report new muscle or tendon pain, neurological symptoms, severe diarrhoea, chest pain, fainting, or allergic signs immediately and stop the medication.
How to use Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)
- Take exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Typical adult dosing for many severe infections is 750 mg every 12 hours; follow your clinician’s instructions.
- Swallow tablets whole with a full glass of water.
- Take ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 4–6 hours after antacids, multivitamins, or supplements containing calcium, magnesium, aluminium, iron, or zinc — these reduce absorption.
- Maintain good hydration to reduce risk of crystalluria.
- Avoid strenuous exercise if you experience tendon pain.
- Complete the prescribed course even if you feel better early, unless advised otherwise.
If you have kidney impairment, dosing adjustments may be required — consult your prescriber.
How Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin) works
Ciprofloxacin targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV — enzymes necessary for DNA replication and repair. Inhibiting these leads to breaks in bacterial DNA and cell death. It is bactericidal and most effective against actively dividing bacteria.
Safety advice
| Allergies | Avoid ciprofloxacin if you have had a severe reaction to fluoroquinolones. |
| Pregnancy | Generally avoided during pregnancy unless there is no safe alternative; discuss with your obstetrician. |
| Breastfeeding | Small amounts pass into breastmilk — consult your clinician before use. |
| Children & adolescents | Use generally restricted due to potential effects on cartilage development; specialist advice required. |
| Tendon risk | Increased risk of tendonitis and rupture — higher in older adults, those on systemic corticosteroids, or with prior tendon disorders. Stop and seek medical advice if tendon pain occurs. |
| Cardiac risk | Caution in patients with known QT prolongation or those on QT-prolonging drugs; ciprofloxacin can increase QT interval in some patients. |
| Drug interactions | Significant interactions with warfarin (bleeding risk), theophylline, some antiarrhythmics, and others — review all medications with your clinician or pharmacist. |
What if you forget to take Cipro 750 mg?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s near the next dose. Do not double doses. Missing doses can reduce treatment effectiveness and promote resistance.
All substitutes
Alternative antibiotics depend on the infection, organism susceptibility and patient factors:
- Levofloxacin (another fluoroquinolone; consider risks and guidelines)
- A broad-spectrum beta-lactam +/- beta-lactamase inhibitor (e.g., piperacillin-tazobactam for severe infections in hospital)
- Third-generation cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime) for certain infections
- Carbapenems (for resistant infections, specialist use)
Choice should be guided by culture & sensitivity and specialist advice for complicated infections.
Quick tips
- Avoid antacids, iron or mineral supplements close to dosing.
- Report tendon pain, numbness, severe diarrhoea, or neurological symptoms immediately.
- Limit exposure to direct sunlight and use sunscreen if photosensitivity occurs.
- Keep well hydrated while taking ciprofloxacin.
Fact Box
| Generic name | Ciprofloxacin |
| Brand | Cipro 750 mg |
| Drug class | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic |
| Form | Oral tablet |
| Typical adult dose | 750 mg every 12 hours for many complicated infections (clinician directed) |
| Prescription | Required |
Patient concerns
Is Cipro 750 mg safe for my UTI? It is commonly used for complicated UTIs when the pathogen is susceptible; local resistance and individual risk factors determine suitability.
How soon will I feel better? Many patients notice improvement within 48–72 hours; if symptoms worsen or fail to improve, contact your clinician.
User feedback
Patients often report rapid symptom relief for urinary and certain GI infections when ciprofloxacin is used appropriately. Reported concerns include gastrointestinal upset, dizziness and, rarely, tendon or neurological effects.
Are you currently taking Cipro 750 mg (Ciprofloxacin)? Let us know how well it is working for you by taking this survey.
FAQs
Can I stop Cipro when I feel better?
No — complete the full prescribed course to reduce relapse and resistance risk unless your clinician advises otherwise.
Can ciprofloxacin cause tendon rupture?
Yes — rare but serious. Risk increases with age, corticosteroid use, and previous tendon disorders. Stop and seek urgent care if you experience tendon pain or difficulty walking.
Can I drink alcohol while taking ciprofloxacin?
Moderate alcohol is not strictly contraindicated, but avoid heavy drinking while unwell; alcohol can increase dizziness and may worsen side effects.
How should I store Cipro 750 mg?
Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and out of reach of children. Do not use past expiry.
Related products
- Levofloxacin 500 mg
- Moxiflox 400 mg
- View all antibiotics
Want to share the information?
Share this article to help others understand appropriate use and safety of ciprofloxacin.
Disclaimer:
This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Ciprofloxacin has rare but serious side effects — consult a healthcare provider before starting or stopping this medicine.
References
- Fluoroquinolone prescribing guidelines and safety communications
- Clinical infectious disease treatment guidance
Marketer details
genericurerx — support@genericurerx.com — www.genericurerx.com
In case of any issues, contact us
Use live chat or our contact page for order support.
Lab tests offered by us
- Urine culture & sensitivity
- Blood cultures (for systemic infection)
- Liver & renal function tests (LFT, KFT)
Additional offers
Use code GLOBAL10 to get 10% off your first order.
What are you using this medicine for?
Select at checkout to receive personalised pharmacist advice.
Know Us
Your trusted online global pharmacy.
Our Policies
Authenticity guarantee • Secure shipping • Privacy focused
Our Services
Worldwide shipping • Pharmacist support • Lab test booking
Connect
Follow us for updates & health information.
Social Links
Facebook • Twitter • Instagram
Want daily dose of health?
Subscribe to our newsletter for verified health tips.
Reliable
Genuine medicines from trusted manufacturers.
Secure
Encrypted checkout and secure delivery.
Affordable
Competitive pricing and special offers.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.